- 2.5.1 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL Yum Repository
- 2.5.2 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL APT Repository
- 2.5.3 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL SLES Repository
- 2.5.4 Installing MySQL on Linux Using RPM Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.5 Installing MySQL on Linux Using Debian Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.6 Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker
- 2.5.7 Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories
- 2.5.8 Installing MySQL on Linux with Juju
- 2.5.9 Managing MySQL Server with systemd
Linux supports a number of different solutions for installing MySQL. We recommend that you use one of the distributions from Oracle, for which several methods for installation are available:
Table 2.8 Linux Installation Methods and Information
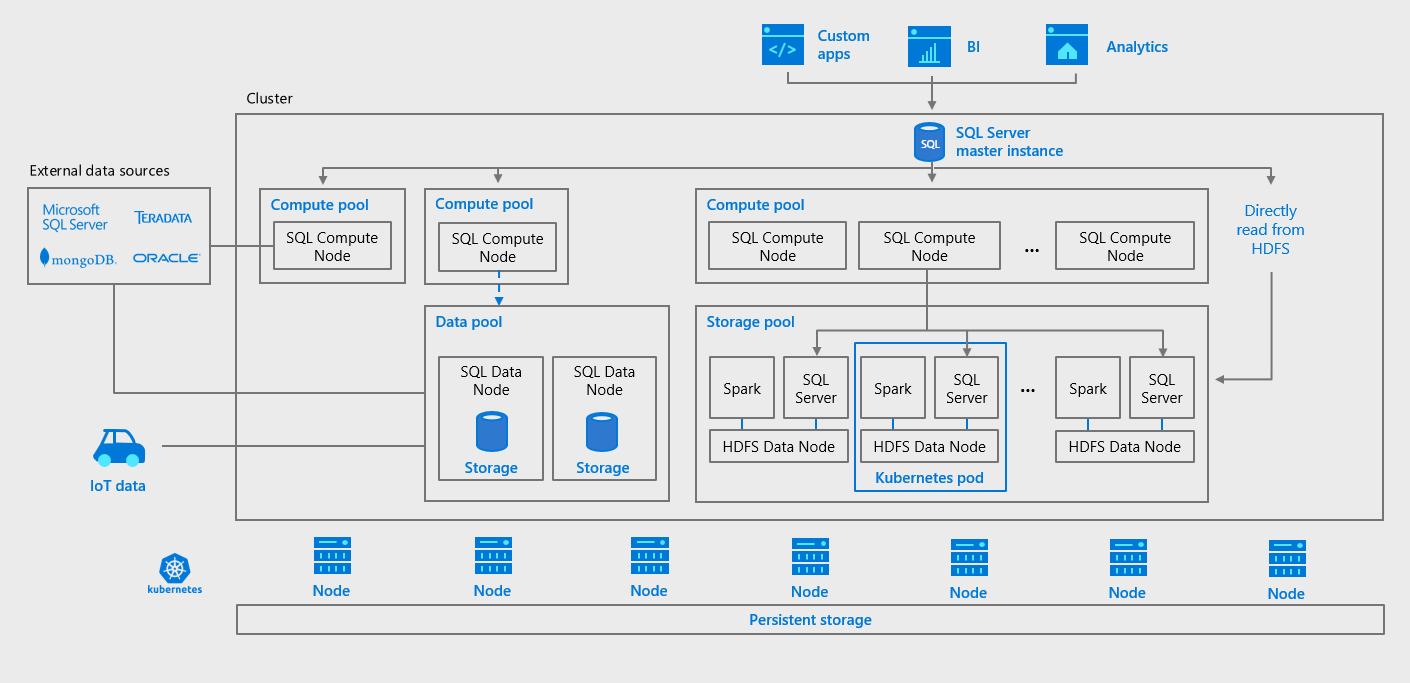
| Type | Setup Method | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Apt | Enable the MySQL Apt repository | Documentation |
| Yum | Enable the MySQL Yum repository | Documentation |
| Zypper | Enable the MySQL SLES repository | Documentation |
| RPM | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| DEB | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| Generic | Download a generic package | Documentation |
| Source | Compile from source | Documentation |
| Docker | Use the Oracle Container Registry. You can also use Docker Hub for MySQL Community Edition and My Oracle Support for MySQL Enterprise Edition. | Documentation |
| Oracle Unbreakable Linux Network | Use ULN channels | Documentation |
- 2.5.1 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL Yum Repository
- 2.5.2 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL APT Repository
- 2.5.3 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL SLES Repository
- 2.5.4 Installing MySQL on Linux Using RPM Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.5 Installing MySQL on Linux Using Debian Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.6 Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker
- 2.5.7 Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories
- 2.5.8 Installing MySQL on Linux with Juju
- 2.5.9 Managing MySQL Server with systemd
Linux supports a number of different solutions for installing MySQL. We recommend that you use one of the distributions from Oracle, for which several methods for installation are available:
Table 2.8 Linux Installation Methods and Information
| Type | Setup Method | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Apt | Enable the MySQL Apt repository | Documentation |
| Yum | Enable the MySQL Yum repository | Documentation |
| Zypper | Enable the MySQL SLES repository | Documentation |
| RPM | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| DEB | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| Generic | Download a generic package | Documentation |
| Source | Compile from source | Documentation |
| Docker | Use the Oracle Container Registry. You can also use Docker Hub for MySQL Community Edition and My Oracle Support for MySQL Enterprise Edition. | Documentation |
| Oracle Unbreakable Linux Network | Use ULN channels | Documentation |
- Install a Linux virtual machine (VM) on our Windows OS, and then Install Docker Community on the VM. I'm going to show you both options and let you choose the best way. Hint: the best way is a.
- On GitHub Oracle created an official software Vagrant Boxes Repository official software Vagrant Boxes Repository, dedicated to Oracle Products running on top of Oracle Linux. Between them you can find ready-to-run VMs with Docker, Container-Registry, Kubernetes, Oracle Database, LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP) and Preview Releases for.
- We and third parties use cookies or similar technologies ('Cookies') as described below to collect and process personal data, such as your IP address or browser information.
Oracle Linux Docker Proxy
2.5.3 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL SLES Repository 2.5.4 Installing MySQL on Linux Using RPM Packages from Oracle 2.5.5 Installing MySQL on Linux Using Debian Packages from Oracle 2.5.6 Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker 2.5.7 Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories 2.5.8 Installing MySQL on Linux with Juju. Get all of Hollywood.com's best Movies lists, news, and more.
Oracle Linux Install Docker
As an alternative, you can use the package manager on your system to automatically download and install MySQL with packages from the native software repositories of your Linux distribution. These native packages are often several versions behind the currently available release. You are also normally unable to install development milestone releases (DMRs), since these are not usually made available in the native repositories. For more information on using the native package installers, see Section 2.5.7, 'Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories'.
Oracle Linux Docker-compose Install
For many Linux installations, you want to set up MySQL to be started automatically when your machine starts. Many of the native package installations perform this operation for you, but for source, binary and RPM solutions you may need to set this up separately. The required script, mysql.server, can be found in the support-files directory under the MySQL installation directory or in a MySQL source tree. You can install it as /etc/init.d/mysql for automatic MySQL startup and shutdown. See Section 4.3.3, 'mysql.server — MySQL Server Startup Script'.
